Understanding Torn Meniscus
The meniscus is a C-shaped piece of cartilage that acts as a shock absorber between your thighbone (femur) and shinbone (tibia). It helps to distribute weight evenly across the knee joint, providing stability and cushioning. A torn meniscus occurs when this cartilage is damaged, often due to a sudden twisting or impact.
Types of Meniscus Tears
There are different types of meniscus tears, each with its own characteristics and causes.
- Horizontal Tear: A horizontal tear occurs when the meniscus is torn across its width, usually due to a twisting injury.
- Radial Tear: A radial tear occurs when the meniscus is torn from the inside out, often due to a direct impact or a sudden forceful movement.
- Flapper Tear: A flapper tear occurs when a piece of the meniscus is torn loose and flaps around, often due to a severe injury.
- Degenerative Tear: Degenerative tears occur over time due to wear and tear on the meniscus, often in older individuals.
Symptoms of a Torn Meniscus
Symptoms of a torn meniscus can vary depending on the severity of the tear. Common symptoms include:
- Pain: Pain in the knee, often on the inside or outside of the joint, that worsens with activity.
- Swelling: Swelling around the knee joint, often noticeable within a few hours of the injury.
- Stiffness: Stiffness in the knee joint, making it difficult to bend or straighten the leg.
- Locking: A feeling of the knee locking or catching, making it difficult to move the joint.
- Clicking: A clicking or popping sound in the knee joint during movement.
Complications of a Torn Meniscus
If left untreated, a torn meniscus can lead to complications such as:
- Arthritis: A torn meniscus can increase the risk of developing osteoarthritis, a condition that causes pain, stiffness, and swelling in the knee joint.
- Further Injury: A torn meniscus can make the knee joint more vulnerable to further injury, especially if the tear is not repaired.
- Loss of Function: A torn meniscus can lead to a loss of function in the knee joint, making it difficult to walk, run, or participate in other activities.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options: Torn Meniscus
So, you’ve got a torn meniscus. It’s like a little tear in the cartilage that cushions your knee joint. No worries, though, we can figure out what’s going on and get you back on your feet!
Diagnosis, Torn meniscus
To diagnose a torn meniscus, your doctor will ask about your symptoms and examine your knee. They might also order some tests to get a clearer picture.
- Physical Examination: Your doctor will assess your range of motion, tenderness, and stability of your knee. They might perform some specific tests to check for a torn meniscus, such as the McMurray test or the Thessaly test.
- Imaging Tests: To confirm the diagnosis, your doctor might recommend an MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging). This provides detailed images of the knee joint and helps identify the location and severity of the tear.
Treatment Options
There are different ways to treat a torn meniscus, depending on the severity of the tear and your individual situation.
Conservative Treatment
- RICE (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation): This is the first line of treatment for most torn meniscus injuries. It helps reduce pain and inflammation.
- Pain Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help manage pain and inflammation. In some cases, your doctor might prescribe stronger pain medications.
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy exercises can help strengthen the muscles around your knee, improve range of motion, and restore stability.
- Bracing: A knee brace can provide support and help stabilize your knee joint.
Surgical Treatment
If conservative treatment doesn’t work, surgery might be an option. There are two main types of surgical procedures for a torn meniscus:
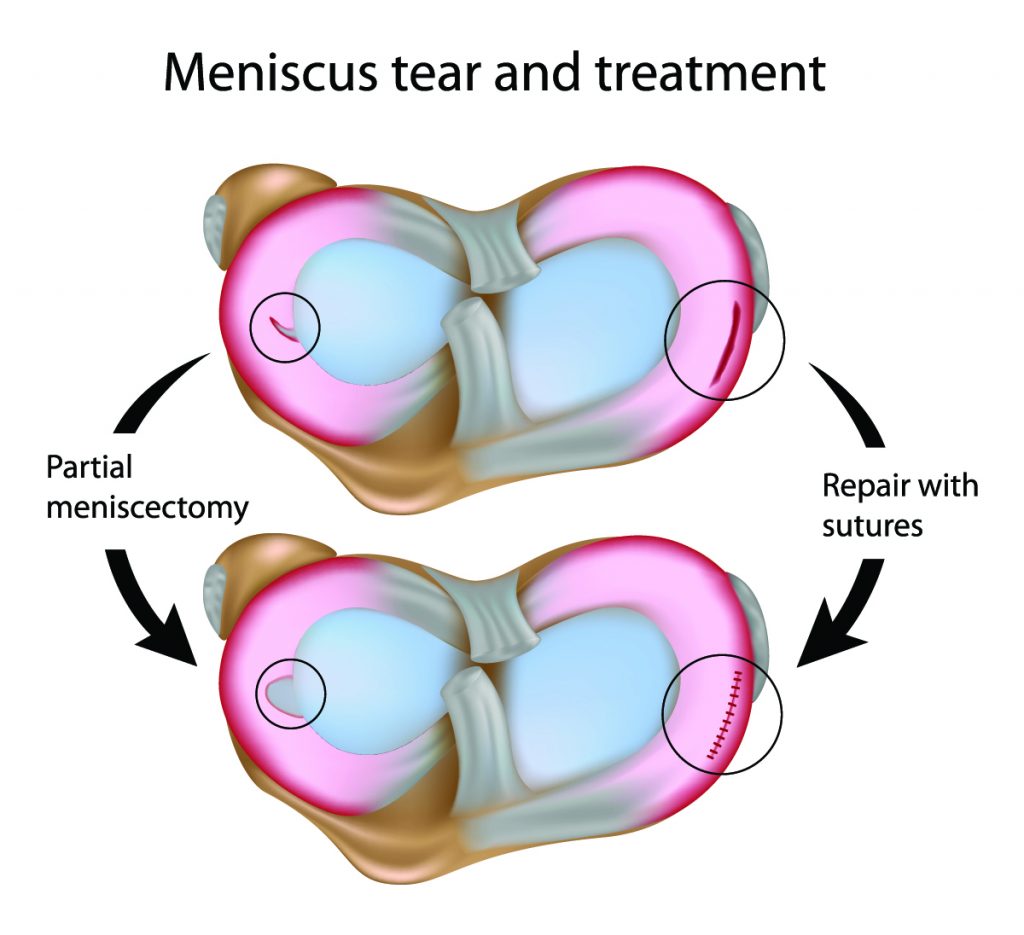
- Meniscectomy: This procedure involves removing the torn portion of the meniscus. It is often performed for larger tears or tears that are causing significant pain or instability.
- Meniscus Repair: This procedure involves stitching the torn meniscus back together. It is usually performed for smaller tears or tears that are in a location that can be repaired.
Comparing Treatment Options
| Treatment Option | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Conservative Treatment | Non-invasive, less risky, less expensive | May not be effective for all types of tears, may take longer to recover |
| Surgical Treatment | Can effectively treat severe tears, may provide long-term relief | Invasive, more risky, more expensive, longer recovery time |
Recovery and Rehabilitation
Recovering from a torn meniscus can be a journey, but with the right approach, you can get back to your active lifestyle. This section delves into the essential aspects of rehabilitation, focusing on a comprehensive program, the role of physical therapy, and managing pain and swelling.
Physical Therapy and Exercises
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in your recovery. It helps regain strength, flexibility, and stability in your knee joint. Your physical therapist will design a personalized program tailored to your specific needs and injury severity.
Here are some common exercises incorporated into a rehabilitation program:
- Range of Motion Exercises: These exercises focus on restoring the full movement of your knee joint. Examples include knee extensions, knee flexions, and gentle circular movements.
- Strengthening Exercises: These exercises build muscle strength around your knee, improving stability and support. Examples include quadriceps and hamstring strengthening exercises, calf raises, and leg presses.
- Balance Exercises: These exercises enhance your balance and coordination, reducing the risk of falls and further injury. Examples include single-leg stance, heel-toe walking, and standing on an unstable surface.
- Proprioceptive Exercises: These exercises improve your body’s awareness of joint position and movement, enhancing stability and coordination. Examples include standing on a balance board, performing exercises with eyes closed, and using wobble boards.
Managing Pain and Swelling
Pain and swelling are common during the recovery process. Your physical therapist will guide you on managing these symptoms effectively.
- Rest: Avoid activities that aggravate your knee pain and swelling. Give your knee time to heal.
- Ice: Apply ice packs to the injured area for 15-20 minutes at a time, several times a day. Ice helps reduce inflammation and pain.
- Compression: Use a compression bandage to help reduce swelling and provide support to your knee.
- Elevation: Keep your leg elevated above your heart whenever possible. This helps reduce swelling by promoting drainage.
- Pain Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help manage pain and inflammation. Consult your doctor for appropriate medication options.
A torn meniscus, a common sports injury, can significantly impact an athlete’s performance. The recovery process often involves physical therapy and, in some cases, surgery. Following the journey of rising star JJ McCarthy, jj mccarthy news highlights the importance of perseverance and dedication in overcoming such setbacks.
A torn meniscus can be a challenging hurdle, but with proper care and determination, athletes can return to their peak performance.
A torn meniscus, a common knee injury, often involves a painful tear in the cartilage that cushions the joint. This injury can be caused by a sudden twist or impact, and depending on the severity, may require surgery. In some cases, a torn meniscus can be accompanied by a gibbs injury , which involves a fracture of the bone that forms the joint.
While both injuries can cause significant pain and discomfort, understanding the specific mechanism of each is crucial for effective diagnosis and treatment.
